This tutorial is intended for those new to building apps in the cloud, such as engineers and web developers, who want to learn key app development concepts as they apply to Cloud de Confiance by S3NS.
Objectives
- Learn basic Cloud de Confiance tools, such as the Cloud de Confiance console and
gcloud. - Deploy your app to Cloud Run.
- Persist your data with Firestore.
- Store file uploads in Cloud Storage.
- Monitor your app using Google Cloud Observability.
Costs
In this document, you use the following billable components of Cloud de Confiance by S3NS:
The instructions in this document are designed to keep your resource usage within the limits of Cloud de Confiance's Always Free tier.
When you finish the tasks that are described in this document, you can avoid continued billing by deleting the resources that you created. For more information, see Clean up.
Before you begin
-
In the Cloud de Confiance console, on the project selector page, select or create a Cloud de Confiance project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
-
Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role
(
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission. Learn how to grant roles.
-
Verify that billing is enabled for your Cloud de Confiance project.
-
To create a Firestore database in Native mode, complete the following steps:
-
In the Cloud de Confiance console, go to the Firestore create database page.
- From the Select a Cloud Firestore mode screen, click Select Native Mode.
- Select a location for your Firestore database. This location setting is the default Cloud de Confiance resource location for your Cloud de Confiance project . This location is used for Cloud de Confiance services in your Cloud de Confiance project that require a location setting, specifically, your default Cloud Storage bucket and your Cloud Run app.
- Click Create Database.
-
In the Cloud de Confiance console, go to the Firestore create database page.
-
Enable the Cloud Run Admin, Cloud Storage, Cloud Logging, and Error Reporting APIs.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission. Learn how to grant roles. -
Clone the sample repo and open the sample application in Cloud Shell:
Go to Cloud ShellCloud Shell provides command-line access to your Cloud de Confiance resources directly from the browser.
- To download the sample code and change into the app directory, click Proceed.
-
In Cloud Shell, configure the
gcloudtool to use your new Cloud de Confiance project:# Configure gcloud for your project gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID
Replace PROJECT_ID with the Cloud de Confiance project ID that you created using the Cloud de Confiance console.
The Google Cloud CLI is the primary way you interact with your Cloud de Confiance resources from the command line. In this tutorial, you use the
gcloudtool to deploy and monitor your app.
Run your app
-
Install your app dependencies using the
npmcommand:npm install -
Run the app:
npm start - In Cloud Shell, click Web preview , and select Preview on port 8080. This opens a new window with your running app.
Deploying your app to Cloud Run
Cloud de Confiance offers several options for running your code. For this example, you use Cloud Run to deploy a scalable app to Cloud de Confiance. Cloud Run doesn't require you to manage servers and automatically scales to support traffic spikes.
- Use Cloud Build to build a Docker container and publish to Container Registry:
gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/
PROJECT_ID/bookshelf .Replace
PROJECT_IDwith the Cloud de Confiance project ID that you created. - Run the container with Cloud Run:
gcloud run deploy bookshelf --image gcr.io/
PROJECT_ID/bookshelf \ --region us-central1 --allow-unauthenticatedYour app is now viewable at the URL displayed in the output of
gcloud run:Service [bookshelf] revision [bookshelf-00001] has been deployed and is serving 100 percent of traffic. Service URL: https://bookshelf-PROJECT-uc.a.run.app
-
Copy the URL into your web browser to view the app.
For more information on deploying to Cloud Run, see the Cloud Run documentation.
Persist your data with Firestore
You cannot store information on your Cloud Run instances, because it is lost if the instance is restarted, and doesn't exist when new instances are created. Instead, you use a database that all your instances read from and write to.
Cloud de Confiance offers several options for storing your data. In this example, you use Firestore to store the data for each book. Firestore is a fully managed, serverless, NoSQL document database that lets you store and query data. Firestore auto scales to meet your app needs, and scales to zero when you're not using it. Add your first book now.
-
To create a book for your deployed app, click Add book.

- In the Title field, enter
Moby Dick. - In the Author field, enter
Herman Melville. -
Click Save. There is now an entry to your Bookshelf app.
-
In the Cloud de Confiance console, to refresh the Firestore page, click
Refresh refresh.
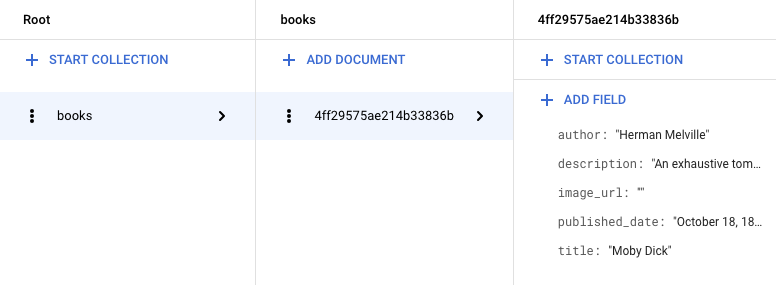
The data appears in Firestore. The Bookshelf app stores each book
as a
Firestore document
with a unique ID, and all these documents are stored in a
Firestore collection.
For the purposes of this tutorial, the collection is called books.
Firestore stores the books by using the Firestore Client Library. Here is an example of fetching a Firestore document:
For more information on using Firestore, see Adding data to Firestore.
Store file uploads in Cloud Storage
Now that you've added a book, it's time to add the book cover image. You cannot store files on your instances. A database isn't the right choice for image files. Instead, you use Cloud Storage.
Cloud Storage is the primary blob store for Cloud de Confiance. You can use Cloud Storage to host app assets that you want to share across Cloud de Confiance. To use Cloud Storage, you need to create a Cloud Storage bucket, a basic container to hold your data.
- In the Cloud de Confiance console, go to the Cloud Storage Browser page.
- Click Create bucket.
- In the Create bucket dialog, enter a name for your bucket by appending your
Cloud de Confiance project ID to the string
_bucketso the name looks likeYOUR_PROJECT_ID_bucket. This name is subject to the bucket name requirements. All other fields can remain at their default values. - Click Create.
- After your bucket is created, objects must be made publicly accessible to be viewed by users. To make your objects publicly accessible see Making Data Public.
-
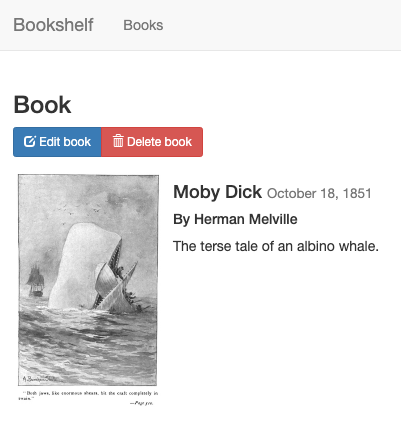
Click Edit book, and select an
image to upload as your book's cover. For example, you can use this public
domain image:

-
Click Save. You're redirected to the
homepage, where there is an entry to your Bookshelf app.
The bookshelf app sends uploaded files to Cloud Storage by using the Cloud Storage Client Library.
For more information on using Cloud Storage, see the Cloud Storage introduction.
Monitor your app using Google Cloud Observability
You've deployed your app and created and modified books. To monitor these events for your users, use Application Performance Management.
Monitor logs with Cloud Logging
-
In the Cloud de Confiance, go to the Logs Explorer
Go to Logs ExplorerYou can monitor your app in real time. If you have any issues with your app, this is one of the first places to look.
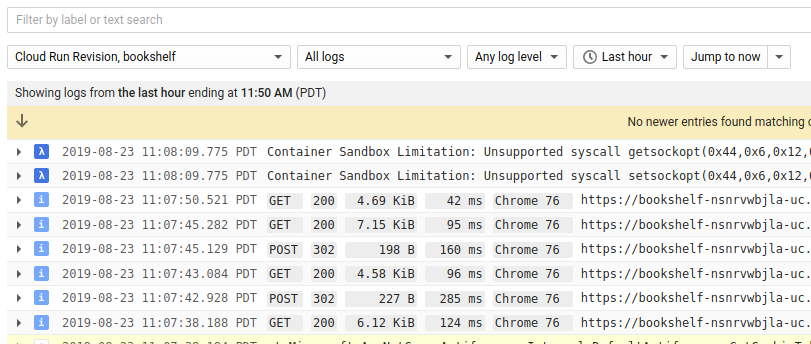
- In the Resource drop-down list, select Cloud Run Revision, bookshelf.
Monitor errors with Error Reporting
-
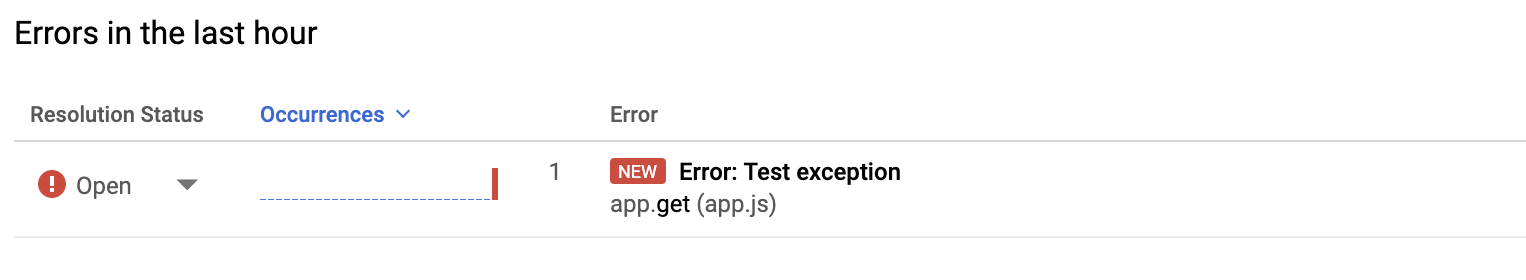
In the Cloud de Confiance console, go to the Error Reporting page.
Go to Error Reporting page
Error Reporting highlights errors and exceptions in your app and lets you set up alerting around them. -
In your browser, go to the
/errorsURL in your app.
YOUR_CLOUD_RUN_URL/errors
This generates a new test exception and sends it to Google Cloud Observability.
-
In the Cloud de Confiance console, return to the Error Reporting page, and in a few moments the new error is visible. Click Auto Reload so you don't need to manually refresh the page.
Clean up
To avoid incurring charges to your Google Cloud account for the resources used in this tutorial, either delete the project that contains the resources, or keep the project and delete the individual resources.
Delete the project
- In the Cloud de Confiance console, go to the Manage resources page.
- In the project list, select the project that you want to delete, and then click Delete.
- In the dialog, type the project ID, and then click Shut down to delete the project.
