Cloud SQL は、MySQL、PostgreSQL、SQL Server 用のフルマネージド リレーショナル データベース サービスです。これにより、データベース管理タスクから解放され、データの管理により多くの時間をかけることができます。
このページでは、 Cloud de Confianceの SQL データ ストレージを提供する Cloud SQL の基本コンセプトと用語について説明します。主なコンセプトの詳細については、主な用語と機能のページをご覧ください。Cloud SQL データベースの比較については、データベース エンジンによる Cloud SQL の機能サポートをご覧ください。
Cloud SQL のユースケース
Cloud SQL は、ローカル MySQL、PostgreSQL、SQL Server データベースの代替となるクラウドベースのサービスです。Cloud SQL を使用することで、データベースの管理にかかる時間を減らし、データベースを使用する時間を増やすことができます。
Compute Engine、App Engine、 Cloud de Confiance by S3NS の他のサービスで実行されている多くのアプリケーションでは、データベース ストレージに Cloud SQL を使用します。
Cloud SQL が提供するもの
Cloud SQL には多数のサービスが用意されているため、そうしたサービスを自分で構築して管理する必要はありません。ユーザーはデータそのものに集中し、次のようなオペレーションを Cloud SQL に任せることができます。
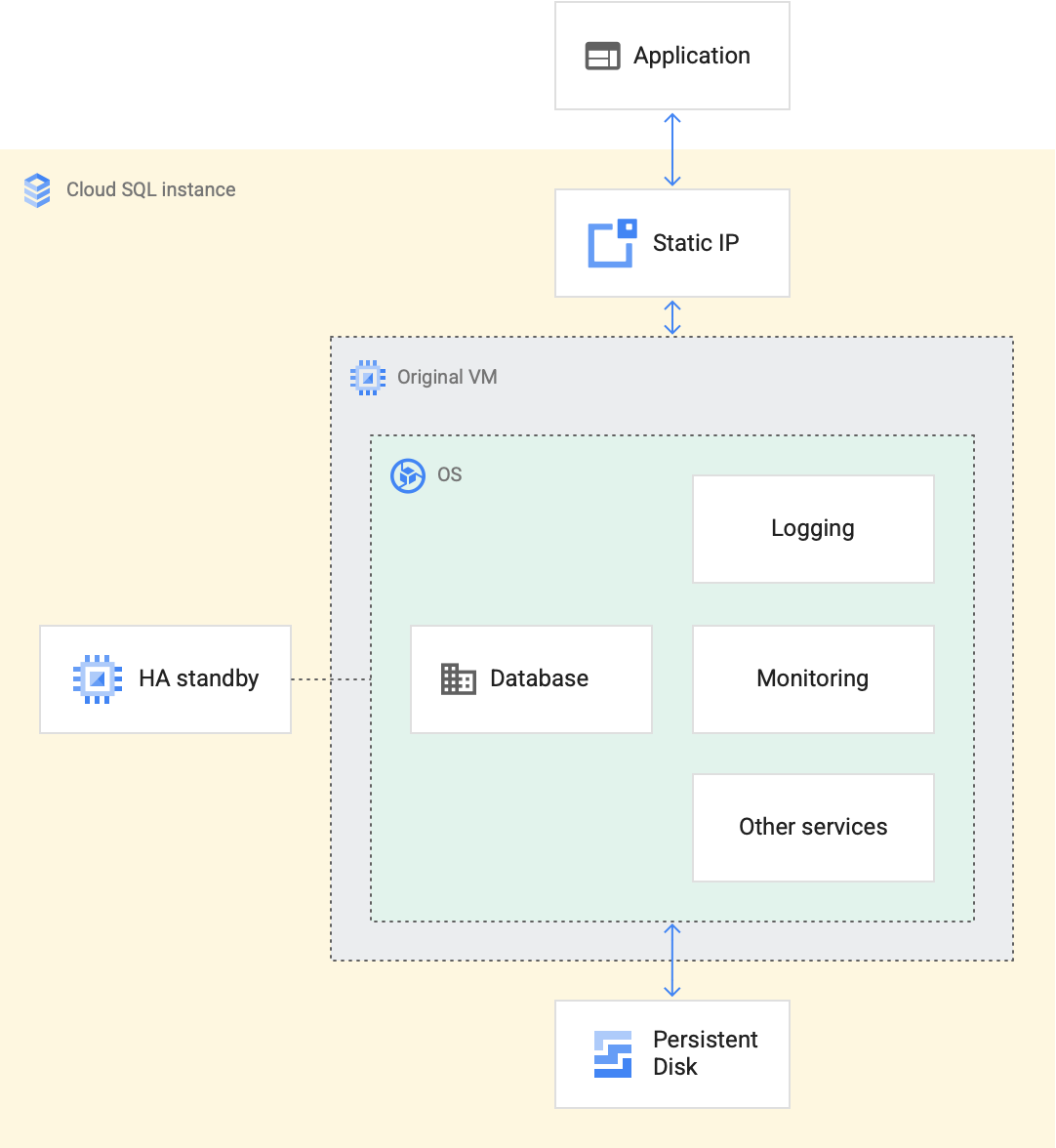
Cloud SQL インスタンスとは
各 Cloud SQL インスタンスは、ホスト Cloud de Confiance サーバー上で実行されている仮想マシン(VM)を利用します。各 VM は、MySQL サーバー、PostgreSQL、SQL Server などのデータベース プログラムと、ロギングやモニタリングなどのサポート サービスを提供するサービス エージェントを運用します。また、高可用性オプションでは、別のゾーンにプライマリ VM と同一の構成を持つスタンバイ VM も用意されています。
データベースは、スケーラビリティと耐久性に優れたネットワーク ストレージ デバイスに保存されます。このデバイスは persistent disk と呼ばれ、VM にアタッチされます。静的 IP アドレスは各 VM に割り当てられ、アプリケーションの接続先の IP アドレスが Cloud SQL インスタンスの全存続期間を通して持続するようにします。
Cloud SQL インスタンスの概要:
データベース管理
Cloud SQL を使ってデータベースとデータベース ユーザーを作成、削除することもできますが、Cloud SQL はデータベース管理ツールではありません。データベース エンジンに応じて、次のようなさまざまなデータベース管理ツールを選択できます。
- MySQL 向けの phpMyAdmin
- MySQL 向けの MySQL Workbench
- MySQL と PostgreSQL 向けの Toad Edge
- PostgreSQL 向けの pgAdmin.org
- SQL Server 向けの SQL Server Management Studio
- SQL Server 向けの Visual Studio Code
Cloud SQL マネージド データベースに接続する
Cloud SQL マネージド データベースへの接続は、セルフマネージド データベースに接続する場合と同様です。Cloud SQL インスタンスは、構成方法に応じて、パブリック IP アドレス(Cloud de Confiance外部からインターネット経由でアクセス可能)またはプライベート IP アドレス(Virtual Private Cloud(VPC)ネットワーク経由でのみアクセス可能)を使用します。さらに、Cloud SQL には Cloud SQL Auth Proxy をはじめ、インスタンスに接続できるユーザーを制御するためのさまざまな認可オプションが用意されています。
Cloud SQL インスタンスに接続して、認証と認可を行う方法については、接続の概要ページをご覧ください。
Cloud SQL の更新
Cloud SQL インスタンスの利用期間中は、次の 2 種類の更新が発生する可能性があります。
- 構成の更新。ユーザーが行った更新。
- Cloud SQL で実行されるシステム更新。
構成の更新
データベースの使用量が増加し、新しいワークロードが追加されるのに応じ、ユーザー側でデータベースの構成を更新できます。構成の更新には、次のようなものがあります。
- コンピューティング リソースの増加
- データベース フラグの変更
- 高可用性の有効化
こうした更新は、Cloud SQL を使用すればボタンをクリックするだけで可能ですが、構成を更新するとなるとダウンタイムが必要な場合があります。ただし、Cloud SQL には、ダウンタイムを最小限に抑えてデータベースを引き続き使用できるようにするオプションがいくつか用意されています。
システムの更新
データベース インスタンスの稼働状態を維持するには、構成の更新以外にも運用上の多くの作業が求められます。サーバーやディスクの交換およびアップグレードが必要ですし、新しい脆弱性が発見された場合には、オペレーティング システムにパッチを適用しなければなりません。データベース ソフトウェア プロバイダが新機能をリリースし、新しい問題を修正するたびに、データベース プログラムをアップグレードする必要も生じます。データベース管理者は通常、システムの信頼性と安全性を保ち、最新の状態に保つために、これらの更新を定期的に実行します。Cloud SQL は、こうした定期的なシステム更新に対応するため、データベースの管理に費やす時間を削減し、優れたアプリケーションを開発するための時間を確保できます。
Cloud SQL がシステム更新を実行するプロセスは、更新されるシステムの部分によって異なります。一般に、Cloud SQL のシステム更新は、ハードウェアの更新、オンラインの更新、メンテナンスの 3 つのカテゴリに分類されます。
ハードウェア更新では、欠陥のあるマシンホストの交換や古いディスクの交換など、物理インフラストラクチャの改善が行われます。Cloud de Confiance により、アプリケーションを中断することなくハードウェアが更新されます。たとえば、データベース サーバーを更新する場合、 Cloud de Confianceではライブ マイグレーションを使用します。これは、VM を実行中のまま、元のホストから新しいホストに確実に移行する高度なテクノロジーです。
オンラインの更新により、VM のデータベース プログラムに隣接するサポート サービス エージェントのソフトウェアが強化されます。この更新は、データベースが稼働してトラフィックを処理している間に実行されます。オンラインの更新によってアプリケーションのダウンタイムが発生することはありません。
メンテナンスにより、オペレーティング システムとデータベース プログラムがアップグレードされます。これらの更新ではインスタンスの再起動が必要になるため、ダウンタイムが発生します。このため、Cloud SQL では、アプリケーションへの影響を最小限に抑えながら、メンテナンスのスケジュールを設定できます。 PostgreSQL 用の Cloud SQL Enterprise Plus エディションまたは MySQL 用の Cloud SQL Enterprise Plus エディションを使用している場合は、ダウンタイムを 1 秒未満のダウンタイムに制限できます。
次のステップ
以下のクイックスタートをお試しください。
