BigQuery JupyterLab-Plug-in verwenden
Wenn Sie Feedback oder Unterstützung für dieses Feature benötigen, senden Sie eine E-Mail an bigquery-ide-plugin@google.com.
In diesem Dokument wird beschrieben, wie Sie das BigQuery-JupyterLab-Plug-in installieren und verwenden, um Folgendes zu tun:
- BigQuery-Daten analysieren
- Verwenden Sie die BigQuery DataFrames API.
- BigQuery DataFrames-Notebook in Cloud Composer bereitstellen
Das BigQuery JupyterLab-Plug-in umfasst alle Funktionen des Dataproc JupyterLab-Plug-ins, z. B. das Erstellen einer Dataproc Serverless-Laufzeitvorlage, das Starten und Verwalten von Notebooks und die Entwicklung mit Apache. Spark, Code bereitstellen und Ressourcen verwalten
BigQuery JupyterLab-Plug-in installieren
So installieren und verwenden Sie das BigQuery JupyterLab-Plug-in:
Prüfen Sie in Ihrem lokalen Terminal, ob Python 3.8 oder höher auf dem System installiert ist:
python3 --versionInitialisieren Sie in Ihrem lokalen Terminal die gcloud CLI:
gcloud initInstallieren Sie Pipenv, ein Tool für virtuelle Python-Umgebungen:
pip3 install pipenvErstellen Sie eine neue virtuelle Umgebung:
pipenv shellInstallieren Sie JupyterLab in der neuen virtuellen Umgebung:
pipenv install jupyterlabInstallieren Sie das BigQuery JupyterLab-Plug-in:
pipenv install bigquery-jupyter-pluginWenn die installierte Version von JupyterLab älter als 4.0.0 ist, aktivieren Sie die Plug-in-Erweiterung:
jupyter server extension enable bigquery_jupyter_pluginSo starten Sie JupyterLab:
jupyter labJupyterLab wird in Ihrem Browser geöffnet.
Projekt- und Regionseinstellungen aktualisieren
Standardmäßig wird Ihre Sitzung in dem Projekt und in der Region ausgeführt, die Sie beim Ausführen von gcloud init festgelegt haben. So ändern Sie die Projekt- und Regionseinstellungen für Ihre Sitzung:
- Klicken Sie im JupyterLab-Menü auf Einstellungen > Google BigQuery-Einstellungen.
Sie müssen das Plug-in neu starten, damit die Änderungen wirksam werden.
Daten auswerten
So arbeiten Sie mit Ihren BigQuery-Daten in JupyterLab:
- Öffnen Sie in der JupyterLab-Seitenleiste den Bereich Dataset Explorer (Datensatz-Explorer): Klicken Sie auf das Symbol für Datensätze
 .
. Wenn Sie ein Projekt maximieren möchten, klicken Sie im Bereich Dataset Explorer neben dem Projektnamen auf den Maximierungspfeil .
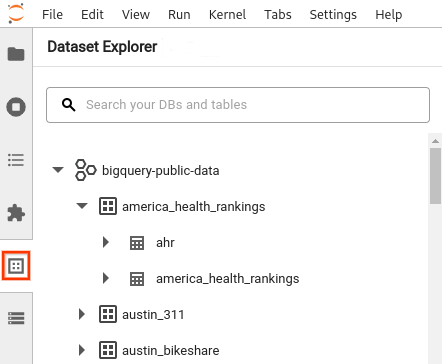
Im Bereich Dataset Explorer werden alle Datasets in einem Projekt angezeigt, die sich in der BigQuery-Region befinden, die Sie für die Sitzung konfiguriert haben. Sie können auf verschiedene Arten mit einem Projekt und einem Dataset interagieren:
- Klicken Sie auf den Namen eines Datasets, um Informationen dazu aufzurufen.
- Zum Aufrufen aller Tabellen in einem Dataset klicken Sie neben dem Dataset auf den Erweiterungspfeil .
- Klicken Sie auf den Namen der Tabelle, um Informationen zu einer Tabelle aufzurufen.
- Zum Ändern des Projekts oder der BigQuery-Region aktualisieren Sie Ihre Einstellungen.
Notebooks ausführen
So fragen Sie Ihre BigQuery-Daten aus JupyterLab ab:
- Klicken Sie auf Datei > Neuer Launcher, um die Launcher-Seite zu öffnen.
- Klicken Sie im Bereich BigQuery-Notebooks auf die Karte BigQuery DataFrames. Es wird ein neues Notebook geöffnet, in dem die ersten Schritte mit BigQuery DataFrames beschrieben werden.
BigQuery DataFrames-Notebooks unterstützen die Python-Entwicklung in einem lokalen Python-Kernel. BigQuery DataFrames-Vorgänge werden aus der Ferne in BigQuery ausgeführt, der Rest des Codes jedoch lokal auf Ihrem Computer. Wenn ein Vorgang in BigQuery ausgeführt wird, werden unter der Codezelle eine Abfragejob-ID und ein Link zum Job angezeigt.
- Klicken Sie auf Job öffnen, um den Job in der Cloud de Confiance Console aufzurufen.
BigQuery DataFrames-Notebook bereitstellen
Sie können ein BigQuery DataFrames-Notebook mithilfe einer serverlosen Dataproc-Laufzeitvorlage in Cloud Composer bereitstellen. Sie müssen mindestens die Laufzeitversion 2.1 verwenden.
- Klicken Sie in Ihrem JupyterLab-Notebook auf calendar_monthJob Scheduler.
- Geben Sie unter Jobname einen eindeutigen Namen für den Job ein.
- Geben Sie unter Umgebung den Namen der Cloud Composer-Umgebung ein, in der Sie den Job bereitstellen möchten.
- Wenn Ihr Notebook parametrisiert ist, fügen Sie Parameter hinzu.
- Geben Sie den Namen der Vorlage für die serverlose Laufzeit ein.
- Geben Sie für die Fehlerbehandlung bei der Notebookausführung eine Ganzzahl für Wiederholungsanzahl und einen Wert (in Minuten) für Wiederholungsverzögerung ein.
Wählen Sie aus, welche Ausführungsbenachrichtigungen gesendet werden sollen, und geben Sie dann die Empfänger ein.
Benachrichtigungen werden über die SMTP-Konfiguration von Airflow gesendet.
Wählen Sie einen Zeitplan für das Notebook aus.
Klicken Sie auf Erstellen.
Wenn Sie Ihr Notebook erfolgreich geplant haben, wird es in der Liste der geplanten Jobs in der ausgewählten Cloud Composer-Umgebung angezeigt.
Nächste Schritte
- BigQuery DataFrames-Kurzanleitung
- Weitere Informationen zur BigQuery DataFrames Python API
- Verwenden Sie JupyterLab für serverlose Batch- und Notebook-Sitzungen mit Dataproc.

