Introduction to notebooks
This document provides an introduction to Colab Enterprise notebooks in BigQuery. You can use notebooks to complete analysis and machine learning (ML) workflows by using SQL, Python, and other common packages and APIs. Notebooks offer improved collaboration and management with the following options:
- Share notebooks with specific users and groups by using Identity and Access Management (IAM).
- Review the notebook version history.
- Revert to or branch from previous versions of the notebook.
Notebooks are BigQuery Studio code assets powered by Dataform. Saved queries are also code assets. All code assets are stored in a default region. Updating the default region changes the region for all code assets created after that point.
Notebook capabilities are available only in the Cloud de Confiance console.
Benefits
Notebooks in BigQuery offer the following benefits:
- BigQuery DataFrames is integrated into notebooks, no setup required. BigQuery DataFrames is a Python API that you can use to analyze BigQuery data at scale by using the pandas DataFrame and scikit-learn APIs.
- Assistive code development powered by Gemini generative AI.
- Auto-completion of SQL statements, the same as in the BigQuery editor.
- The ability to save, share, and manage versions of notebooks.
- The ability to use matplotlib, seaborn, and other popular libraries to visualize data at any point in your workflow.
- The ability to write and execute SQL in a cell that can reference Python variables from your notebook.
- Interactive DataFrame visualization that supports aggregation and customization.
Notebook gallery
The notebook gallery is a central hub for discovering and using prebuilt notebook templates. These templates let you perform common tasks like data preparation, data analysis, and visualization. Notebook templates also help you explore BigQuery Studio features, manage workflows, and promote best practices.
You can use notebook gallery templates to streamline your entire intent-to-insights workflow across each stage of the data lifecycle-from ingestion and exploration to advanced analytics and BigQuery ML.
The notebook gallery provides templates for every skill level. The gallery includes fundamental templates for SQL, Python, Apache Spark, and DataFrames. You can also explore topics like generative AI and multimodal data analytics in BigQuery.
To get started with the notebook gallery, follow these steps:
Go to the BigQuery page.
From from the BigQuery Studio home page, click View notebook gallery.

For more information on using notebook gallery templates, see Create a notebook using the notebook gallery.
Runtime management
BigQuery uses Colab Enterprise runtimes to run notebooks.
A notebook runtime is a Compute Engine virtual machine allocated to a particular user to enable code execution in a notebook. Multiple notebooks can share the same runtime. However, each runtime belongs to only one user and can't be used by others. Notebook runtimes are created based on template, which are typically defined by users with administrative privileges. You can change to a runtime that uses a different template type at any time.
Notebook security
You control access to notebooks by using Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles. For more information, see Grant access to notebooks.
To detect vulnerabilities in Python packages that you use in your notebooks, install and use Notebook Security Scanner (Preview).
Supported regions
BigQuery Studio lets you save, share, and manage versions of notebooks. The following table lists the regions where BigQuery Studio is available:
| Region description | Region name | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Africa | |||
| Johannesburg | africa-south1 |
||
| Americas | |||
| Columbus | us-east5 |
||
| Dallas | us-south1 |
|
|
| Iowa | us-central1 |
|
|
| Las Vegas | us-west4 |
||
| Los Angeles | us-west2 |
||
| Mexico | northamerica-south1 |
||
| Montréal | northamerica-northeast1 |
|
|
| North Virginia | us-east4 |
||
| Oklahoma | us-central2 |
|
|
| Oregon | us-west1 |
|
|
| Salt Lake City | us-west3 |
||
| Santiago | southamerica-west1 |
|
|
| São Paulo | southamerica-east1 |
|
|
| South Carolina | us-east1 |
||
| Toronto | northamerica-northeast2 |
|
|
| Asia Pacific | |||
| Bangkok | asia-southeast3 |
||
| Delhi | asia-south2 |
||
| Hong Kong | asia-east2 |
||
| Jakarta | asia-southeast2 |
||
| Melbourne | australia-southeast2 |
||
| Mumbai | asia-south1 |
||
| Osaka | asia-northeast2 |
||
| Seoul | asia-northeast3 |
||
| Singapore | asia-southeast1 |
||
| Sydney | australia-southeast1 |
||
| Taiwan | asia-east1 |
||
| Tokyo | asia-northeast1 |
||
| Europe | |||
| Belgium | europe-west1 |
|
|
| Berlin | europe-west10 |
||
| Finland | europe-north1 |
|
|
| Frankfurt | europe-west3 |
||
| London | europe-west2 |
|
|
| Madrid | europe-southwest1 |
|
|
| Milan | europe-west8 |
||
| Netherlands | europe-west4 |
|
|
| Paris | europe-west9 |
|
|
| Stockholm | europe-north2 |
|
|
| Turin | europe-west12 |
||
| Warsaw | europe-central2 |
||
| Zürich | europe-west6 |
|
|
| Middle East | |||
| Dammam | me-central2 |
||
| Doha | me-central1 |
||
| Tel Aviv | me-west1 |
||
Pricing
For pricing information about BigQuery Studio notebooks, see Notebook runtime pricing.
Monitor slot usage
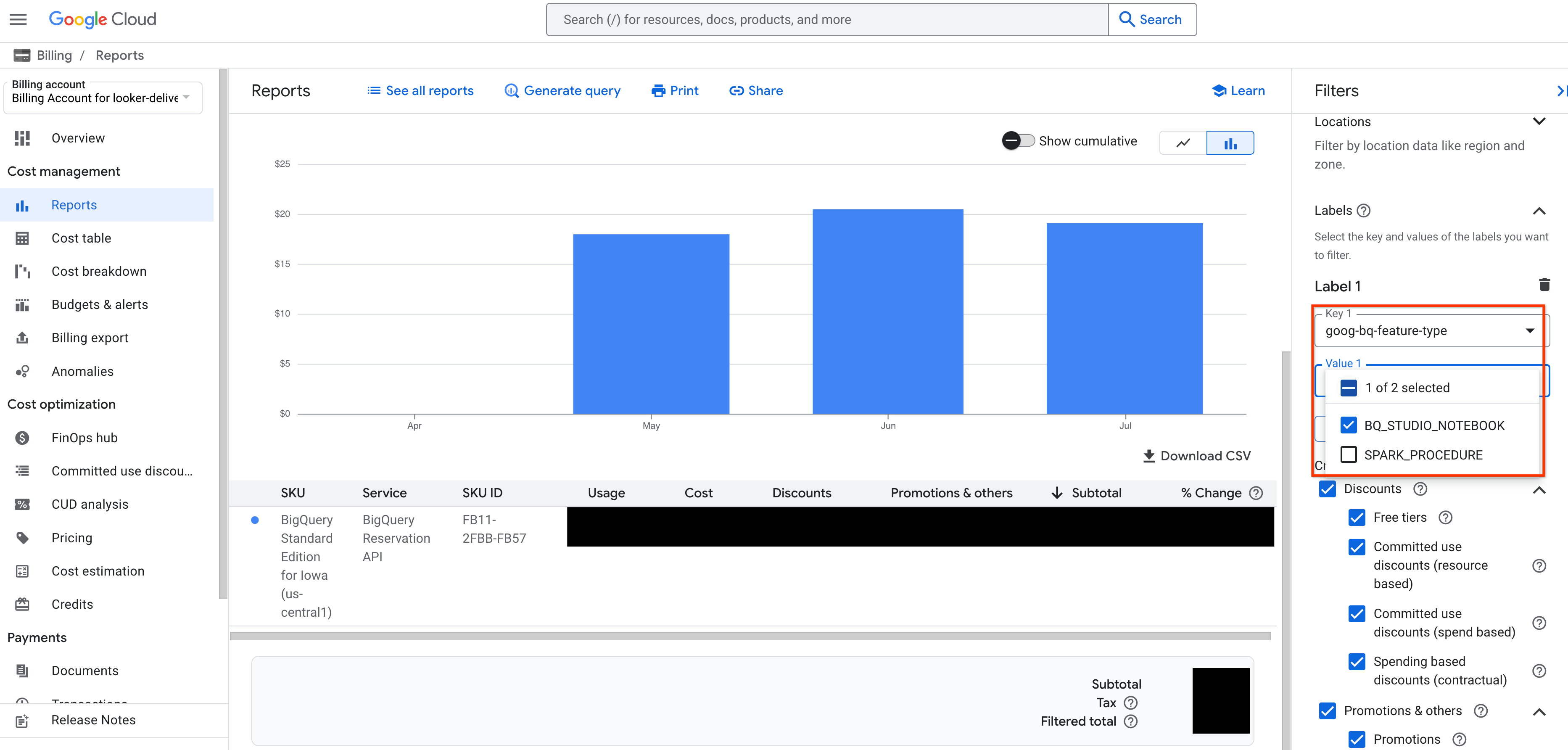
You can monitor your BigQuery Studio notebook slot usage by viewing your Cloud Billing report in the Cloud de Confiance console. In the Cloud Billing report, apply a filter with the label goog-bq-feature-type with the value BQ_STUDIO_NOTEBOOK to view slot usage and costs from BigQuery Studio notebook.
Troubleshooting
For more information, see Troubleshoot Colab Enterprise.
What's next
- Learn how to create notebooks.
- Learn how to manage notebooks.
