Load and query data
Get started with BigQuery by creating a dataset, loading data into a table, and querying the table.
Before you begin
-
In the Cloud de Confiance console, on the project selector page, select or create a Cloud de Confiance project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
-
Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role
(
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission. Learn how to grant roles.
-
If you're using an existing project for this guide, verify that you have the permissions required to complete this guide. If you created a new project, then you already have the required permissions.
-
Enable the BigQuery API.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission. Learn how to grant roles.For new projects, the BigQuery API is automatically enabled.
- Optional: Enable billing for the project. If you don't want to enable billing or provide a credit card, the steps in this document still work. BigQuery provides you a sandbox to perform the steps. For more information, see Enable the BigQuery sandbox.
Required roles
To get the permissions that you need to create a dataset, create a table, load data, and query data, ask your administrator to grant you the following IAM roles on the project:
-
Run load jobs and query jobs:
BigQuery Job User (
roles/bigquery.jobUser) -
Create a dataset, create a table, load data into a table, and query a table:
BigQuery Data Editor (
roles/bigquery.dataEditor)
For more information about granting roles, see Manage access to projects, folders, and organizations.
You might also be able to get the required permissions through custom roles or other predefined roles.
Create a BigQuery dataset
Use the Cloud de Confiance console to create a dataset to store the data. You create your dataset in the US multi-region location. For information on BigQuery regions and multi-regions, see Locations.
- In the Cloud de Confiance console, open the BigQuery page. Go to BigQuery
- In the left pane, click Explorer.
- In the
Explorer pane, click your project name. - Click View actions.
- Select Create dataset.
- On the Create dataset page, do the following:
- For Dataset ID, enter
babynames. - For Location type, select Multi-region, and then choose
US (multiple regions in United States). The public datasets are
stored in the
usmulti-region location. For simplicity, store your dataset in the same location. - Leave the remaining default settings as they are, and click
Create dataset .
Download the file that contains the source data
The file that you're downloading contains approximately 7 MB of data about popular baby names. It's provided by the US Social Security Administration.For more information about the data, see the Social Security Administration's Background information for popular names.
Download the US Social Security Administration's data by opening the following URL in a new browser tab:
https://www.ssa.gov/OACT/babynames/names.zipExtract the file.
For more information about the dataset schema, see the zip file's
NationalReadMe.pdffile.To see what the data looks like, open the
yob2024.txtfile. This file contains comma-separated values for name, assigned sex at birth, and number of children with that name. The file has no header row.Note the location of the
yob2024.txtfile so that you can find it later.
Load data into a table
Next, load the data into a new table.
- In the left pane, click Explorer.
- In the
Explorer pane, expand your project name. - Click Datasets and then next to the babynames dataset, click View actions and select Open.
- Click
Create
table.
Unless otherwise indicated, use the default values for all settings.
- On the Create table page, do the following:
- In the Source section, for
Create table from , choose Upload from the list. - In the Select file field, click Browse.
- Navigate to and open your local
yob2024.txtfile, and click Open. - From the
File format list, choose CSV. - In the Destination section, in the
Table field, enternames_2024. - In the Schema section, click the
Edit as text toggle, and paste the following schema definition into the text field: - Click
Create table .Wait for BigQuery to create the table and load the data.
name:string,assigned_sex_at_birth:string,count:integerPreview table data
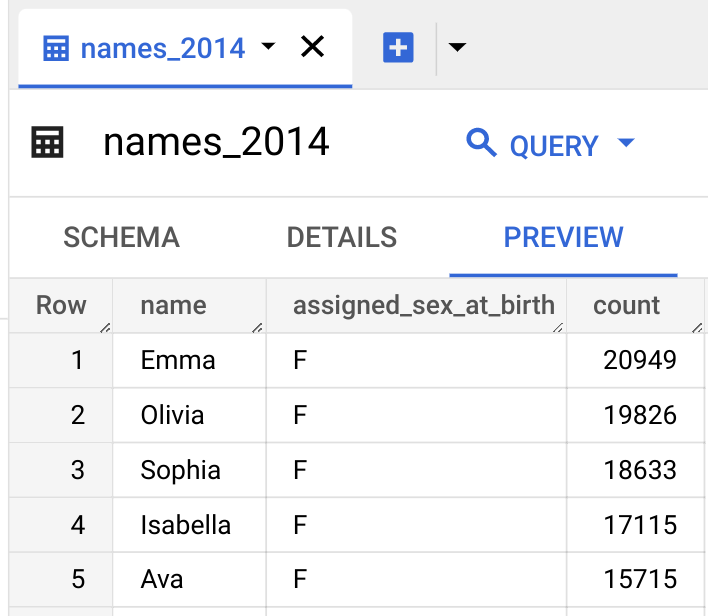
To preview the table data, follow these steps:
- In the left pane, click Explorer.
- In the
Explorer pane, expand your project and click Datasets. - Click the
babynamesdataset, and then select thenames_2024table. - Click the
Preview tab. BigQuery displays the first few rows of the table.
Query table data
Next, query the table.
- Next to the names_2024 tab, click the SQL query option. A new editor tab opens.
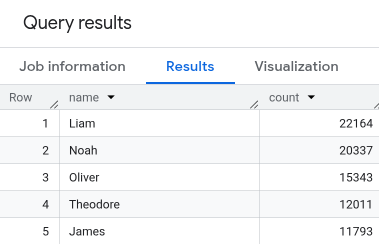
- In the query editor, paste the following query. This query retrieves the
top five names for babies born in the US that were assigned male at birth in
2024.
SELECT name, count FROM `babynames.names_2024` WHERE assigned_sex_at_birth = 'M' ORDER BY count DESC LIMIT 5; - Click
Run . The results are displayed in the Query results section.
You have successfully queried a table in a public dataset and then loaded your sample data into BigQuery using the Cloud de Confiance console.
Clean up
To avoid incurring charges to your Cloud de Confiance account for the resources used on this page, follow these steps.
- In the Cloud de Confiance console, open the BigQuery page. Go to BigQuery
- In the left pane, click Explorer.
- In the Explorer pane, click Datasets and then click the
babynamesdataset that you created. - Expand the View actions option and click Delete.
- In the Delete dataset dialog, confirm the delete command: type the word
deleteand then click Delete.
What's next
- To learn more about loading data into BigQuery, see Introduction to loading data.
- To learn more about querying data, see Overview of BigQuery analytics.
- To learn how to load a JSON file with nested and repeated data, see Loading nested and repeated JSON data.
- To learn more about accessing BigQuery programmatically, see the REST API reference or the BigQuery client libraries page.
