This document gives an overview of future reservation requests in calendar mode.
Use future reservation requests in calendar mode to obtain high-demand resources, such as for creating virtual machine (VM) instances that have GPUs or TPUs attached. When Cloud de Confiance by S3NS approves a reservation request, Compute Engine provisions your reserved resources at your specified date and time, and for a duration of up to 90 days. You can then use the reserved resources for creating GPU VMs, H4D VMs, or TPU VMs to run the following workloads:
Model pre-training jobs
Model fine-tuning jobs
High performance computing (HPC) simulation workloads
Short-term expected increases in inference workloads
For more information about other ways to reserve resources in Compute Engine, see Choose a reservation type.
Create a request in calendar mode
The following sections explain how to view resource availability, as well as what details to specify when you create a future reservation request in calendar mode.
View resource future availability
Before you create a future reservation request in calendar mode, you can view the future availability in a region of the following resources:
For GPU or H4D VMs, up to 60 days in advance
For TPUs, up to 120 days in advance
Compute Engine uses the Dynamic Workload Scheduler (DWS) to view when your requested resources are available. When you create a request, specify the number, type, and reservation period for the resources that you confirmed as available. Cloud de Confiance is more likely to approve your request if you supply this information.
Define request properties
When you create a future reservation request in calendar mode, you must specify the following properties:
Auto-delete. This property determines if Compute Engine deletes the automatically created (auto-created) reservation for your request at the end time, even if the reservation isn't fully consumed. To create a request in calendar mode, you must enable the auto-delete option.
Consumption type. This property defines how VMs consume the auto-created reservation. When you create a request in calendar mode, you must specify that you want to create specifically-targeted reservations. This setting means that only VMs that target the reservation can consume it.
Deployment type. This property defines the collocation of your reserved resources. Compute Engine reserves resources based on the resource type:
For GPU or H4D VMs, you must specify the dense (
DENSE) deployment type when you create a request. This configuration specifies to densely reserve resources for minimal network latency.For TPUs, Compute Engine uses the flexible (
FLEXIBLE) deployment type by default. This configuration specifies to reserve resources as close as possible on a best-effort basis.
Name. The name of your request, which must be unique within your project.
Number of resources. The number of GPU or H4D VMs or TPUs to reserve at your requested start time.
Planning status. This property defines if you immediately submit your request to Cloud de Confiance for review, or save it as a draft and submit it later. When you create a request in calendar mode, you must specify to immediately submit the request for review.
Reservation mode. This property defines the method to reserve resources, which you must set to
CALENDARfor a request in calendar mode.Reservation name. The name for the reservation that Compute Engine automatically creates if Cloud de Confiance approves your request.
Share type. This property defines if other projects in your organization can consume the auto-created reservation for your approved request. You can specify one of the following options:
Single-project. Only your project can consume the reserved capacity.
Shared. You can share the reserved capacity with up to 100 other projects in your organization. If you specify this option, then you must specify the projects to share the auto-created reservation with. For more information, see the best practices for shared reservations.
Reservation period. The date and time when Compute Engine provisions your requested capacity, and you can consume it. The reservation period includes the following:
Start time. When you want to start consuming your reserved capacity. Based on the resources that you reserve, the start time must be at least one of the following values from when you create and submit a request:
For GPU and H4D VMs, 87 hours (three days and 15 hours)
For TPUs, six hours
End time. When your requested capacity is no longer reserved for you. At this time, Compute Engine deletes the auto-created reservation, and stops or deletes any VMs that consume the reservation based on the termination action that you specified for the VMs.
Resource properties. The hardware requirements of the GPU VMs, H4D VMs, or TPUs that you want to reserve. VMs can only use a reservation if their properties match the reservation's properties. For more information, see the requirements to consume reservations.
Workload type. If you reserve TPU v5e, then you must specify how to reserve capacity based on your workload type:
Batch. For workloads that handle large amounts of data in single or multiple operations, such as machine learning (ML) training workloads.
Serving. For workloads that handle concurrent requests and require minimal network latency, such as ML inference workloads.
Zone. The zone where you want to reserve capacity.
Request review process
To reserve capacity by using a future reservation request in calendar mode, you must create and submit the request to Cloud de Confiance for review. After you create and submit a request, Cloud de Confiance reviews it within a minute, and then one of the following occurs:
Cloud de Confiance approves your request: Compute Engine reserves your requested resources and, within a minute after approval, automatically creates an empty reservation. At the request start time, Compute Engine provisions your requested capacity by increasing the number of GPU VMs, H4D VMs, or TPUs in the reservation.
You encounter an error. The request fails because the request's zone lacks sufficient resources. We recommend that you view future resource availability again, and then create and submit a new request for review.
Request lifecycle
The following diagram shows the different states that Compute Engine can set a future reservation request in calendar mode to:
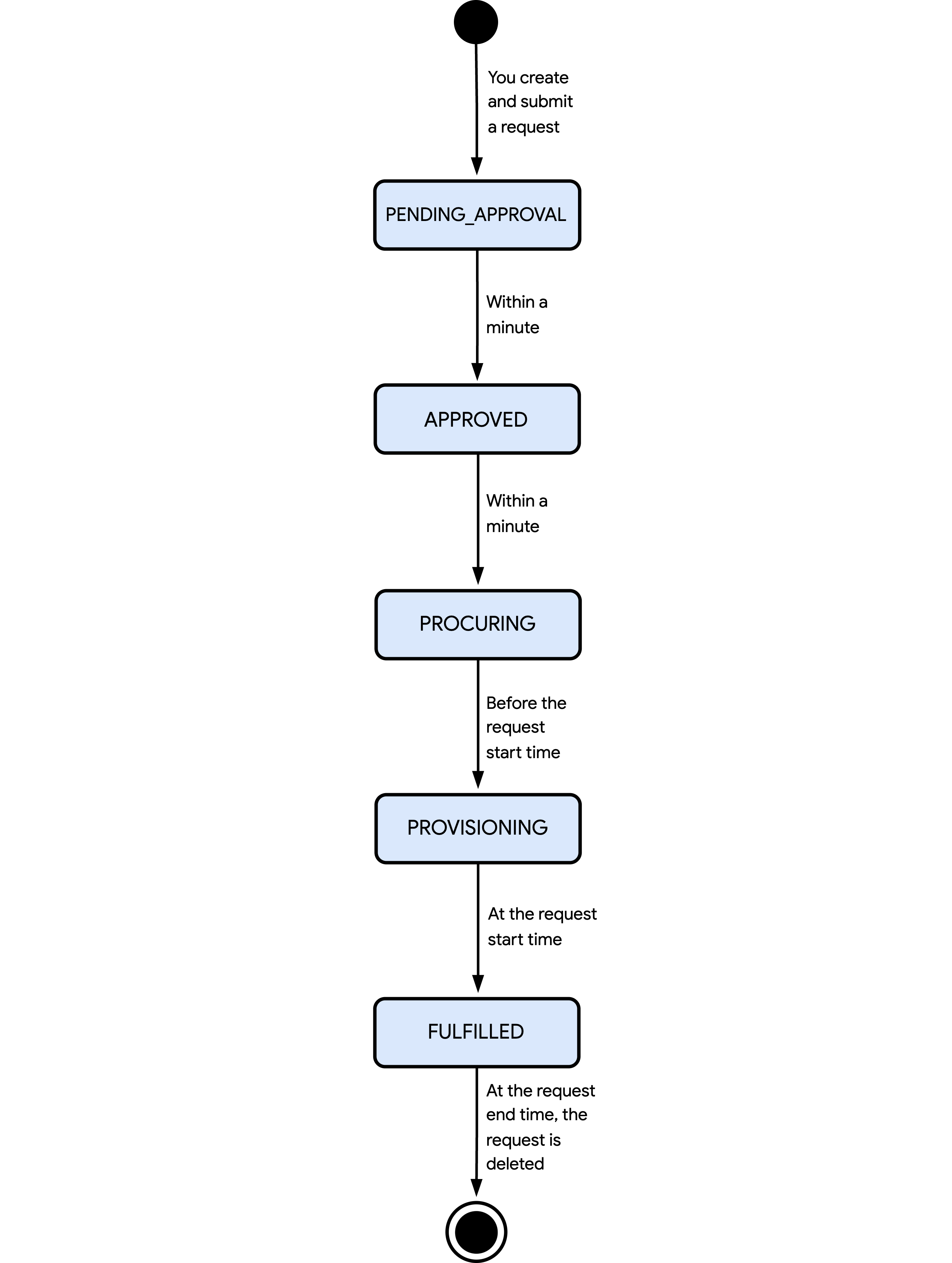
The states and flow of events shown in the preceding diagram are as follows:
PENDING_APPROVAL: you created and submitted a request for review. Within a minute, Cloud de Confiance approves the request.APPROVED: Cloud de Confiance approved your request. Then, within a minute, Compute Engine automatically creates an empty reservation and changes the request state toPROCURING.PROCURING: Compute Engine schedules the provisioning of your reserved resources. Before the request start time, the request state changes toPROVISIONING.PROVISIONING: Compute Engine is provisioning your reserved resources by increasing the number of reserved GPU VMs, H4D VMs, or TPUs in the auto-created reservation. At the request start time, the request state changes toFULFILLED.FULFILLED: Compute Engine has provisioned your reserved resources, and you're charged for them. You can consume the auto-created reservation by creating VMs until the request end time.
At the request end time, Compute Engine deletes the request and the auto-created reservation. It also stops or deletes any VMs that consume the reservation based on the termination action that you specified for the VMs.
Consume provisioned capacity
After Cloud de Confiance approves a future reservation request in calendar mode, Compute Engine automatically creates a reservation with the following characteristics:
The auto-created reservation has no reserved GPU VMs, H4D VMs, or TPUs; you can't consume it yet.
The auto-created reservation inherits the VM or TPU properties specified in your request.
At the request start time, Compute Engine provisions your requested capacity by increasing the number of GPU VMs, H4D VMs, or TPUs in the auto-created reservation. You can then consume the reservation by creating GPU VMs, H4D VMs, or TPU VMs that meet all of the following conditions:
The VMs and the reservation have matching properties.
The VMs specifically target the reservation.
The VMs use the reservation-bound provisioning model.
The VMs must be stopped or deleted at the reservation end time.
You can create VMs until the reservation is fully consumed or until the request end time. At the request end time, Compute Engine deletes the auto-created reservation, and stops or deletes any VMs that consume the reservation.
Quota
Future reservation requests in calendar mode must use the reservation-bound provisioning model. This model doesn't require Compute Engine quota to reserve resources. However, before you create a request, verify that you have sufficient quota for any resources that aren't part of a reservation when you create VMs, such as disks or IP addresses.
Pricing
When you create and submit a future reservation request in calendar mode, and Cloud de Confiance approves your request, you don't immediately incur charges. Instead, you incur charges when the following occurs:
Compute Engine provisions your requested capacity. When your request reaches the
FULFILLEDstate at the request's start time, you incur charges for the provisioned resources according to DWS pricing. This pricing model offers vCPUs, memory, GPUs, and TPUs at a discounted price compared to standard pricing.You use resources outside of the reservation. When you create VMs that consume an auto-created reservation, you don't incur additional charges for the consumed resources. You only incur charges for resources that aren't part of the reservation, such as disks or IP addresses.
You stop incurring charges for the reserved resources at the request end time. At this time, Compute Engine deletes the auto-created reservation, and stops or deletes any VMs that consume the reservation based on their termination action.
Limitations
The following sections explain the limitations for future reservation requests in calendar mode.
Limitations for all requests
All future reservation requests in calendar mode have the following limitations:
You can reserve resources for a period between 1 and 90 days.
After you create and submit a request, you can't cancel, delete, or modify your request.
Limitations for requests for VMs
You can only reserve GPU VMs or H4D VMs as follows:
You can reserve the following number of VMs per request:
For GPU VMs, between 1 and 80 VMs
For H4D VMs, between 1 and 256 VMs
You can reserve the following machine series:
You can reserve GPU VMs only in specific zones. For H4D regional availability, see Available regions and zones and use the Machine series filter to view only the zones where you can reserve H4D instances.
You can't use an instance template to create requests for GPU or H4D VMs.
Limitations for requests for TPUs
You can only reserve TPUs as follows:
You can reserve 1, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, or 1,024 TPU chips per request.
You can reserve the following TPU versions:
You can only reserve 1, 4, or 8 TPU v5e chips for serving (
SERVING) workload types.You can reserve TPUs only in the following zones:
TPU7x:
us-central1-c
TPU v6e:
asia-northeast1-beurope-west4-aus-east5-aus-east5-bus-south1-ai1b
TPU v5p:
us-east5-a
TPU v5e:
For batch (
BATCH) workload types:europe-west4-bus-west4-b
For serving (
SERVING) workload types:us-south1-a
Limitations for all auto-created reservations
An auto-created reservation for a request has the following limitations:
You can only modify the reservation as follows:
To allow or disallow Vertex AI jobs from consuming it.
After the reservation start time.
You can't apply committed use discounts (CUDs) or sustained use discounts (SUDs) to the reservation.
You can't delete the reservation; Compute Engine deletes it at the end time for the reservation.
