This document describes the different reservation types that you can use to reserve capacity for Compute Engine instances. To learn more about the resources that you use to create instances, see Compute Engine instances.
Reservations help ensure that you have the available resources to create instances with the same hardware (memory and vCPUs) and optional resources (GPUs, H4D HPC clusters, TPUs, or Local SSD disks) whenever you need them. Reservations offer the following benefits:
High assurance of capacity: you reserve resources to accommodate for future increases in demand, such as the following:
Growth
Planned or unplanned spikes in usage
Large migrations
Backup and disaster recovery
Exclusive access: reservations prevent others from using your reserved resources.
Inherited properties: reservations inherit the same properties as your chosen machine family.
After you reserve capacity, you can use it to create instances that match the reservation. You don't incur any additional charges when you create these instances. You only pay for resources that aren't part of the reservation, such as disks or IP addresses.
Limitations
All reservation types have the following limitations:
Reservations are zone-specific resources.
You can't use your reserved capacity to create the following Compute Engine resources:
f1-microandg1-smallmachine typesFlex-start VMs
Sole-tenant nodes
Spot VMs or preemptible instances
Choose a reservation type
The following diagram helps you choose the Compute Engine reservation type that best fits your workload's needs:
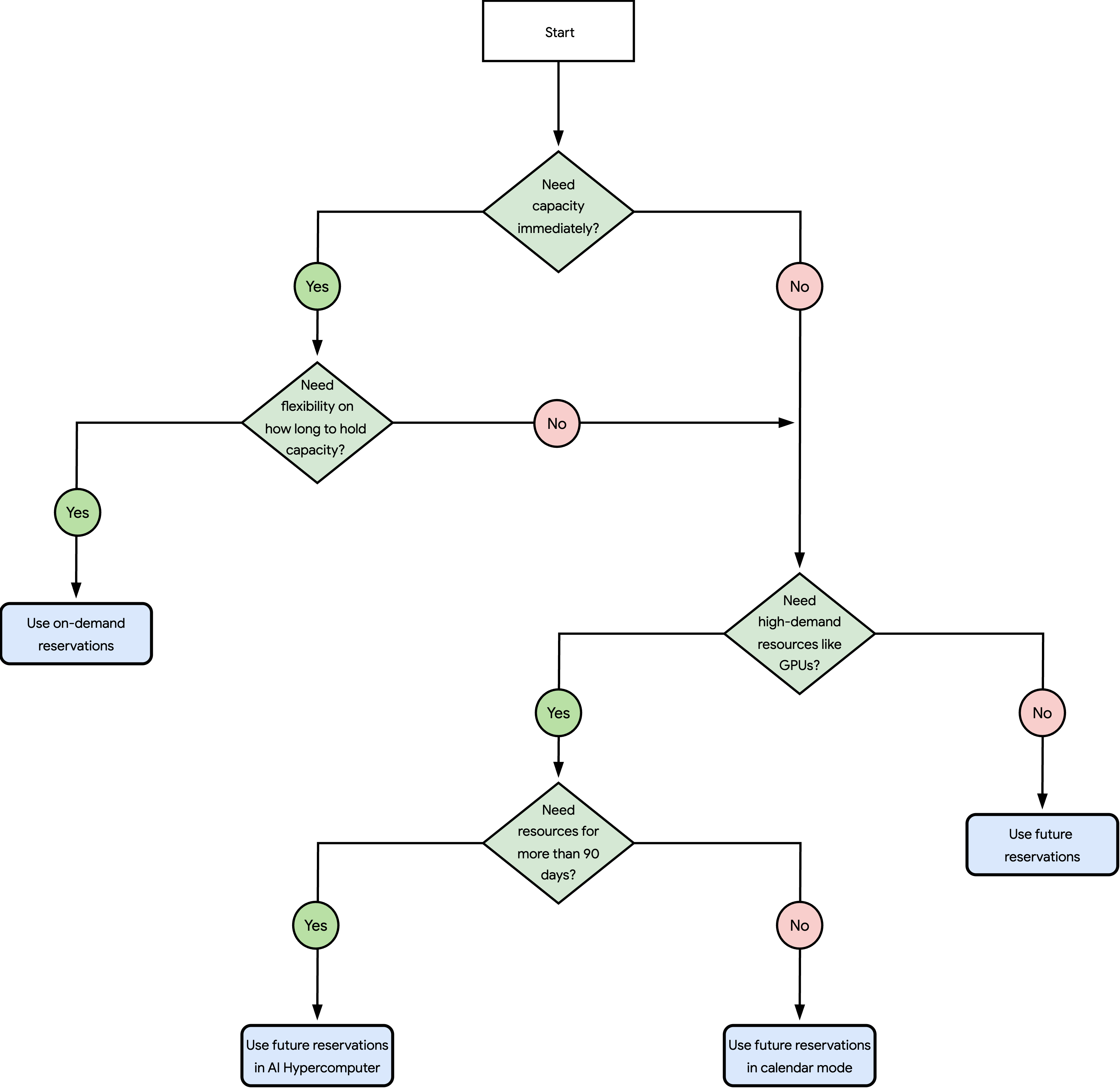
The questions in the preceding diagram are as follows:
Do you need capacity right away?
Yes: Go to the next question.
No: Go to question 3.
Do you need flexibility on how long to hold capacity?
Yes: See Use on-demand reservations.
No: Go to the next question.
Do you need high-demand resources like GPUs?
Yes: Go to the next question.
No: See Use future reservations.
Do you need resources for more than 90 days?
Yes: See Use future reservations in AI Hypercomputer or for H4D, see Reserve capacity through your account team.
Use on-demand reservations
With on-demand reservations, you can reserve capacity for compute instances and get it as soon as you reserve it. After you create an on-demand reservation, you can consume, modify, or delete it whenever you need to.
For more information, see About reservations.
Use future reservations
To reserve instances for a set period, you can use future reservations. After you create a reservation request, you must submit it to Cloud de Confiance by S3NS for review. Cloud de Confiance typically takes five days to review your request. If your request is approved, then Compute Engine creates on-demand reservations with your requested capacity on your chosen date and time. To consume these reservations, you create compute instances that use the reservations. After the reservation period ends, you can modify or delete the reservations.
For more information, see About future reservation requests.
Use future reservations in calendar mode
To reserve GPU instances, H4D instances, or TPUs for up to 90 days, you can use future reservations in calendar mode. To create this type of reservation, first view when your chosen number and type of resources are available in a region. Then, create and submit a reservation request with the properties that you confirmed as available. If you can successfully create the request, then Cloud de Confiance approves it within a minute. After the request is approved, Compute Engine does the following:
Compute Engine creates an on-demand reservation.
Compute Engine reserves your requested resources as close to each other as possible to minimize network latency.
At the start of your reservation period, you can consume the reservation by creating GPU, H4D, or TPU instances. At the end of the reservation period, Compute Engine deletes the reservation, and stops or deletes any instances that consume the reservation based on the termination action that you specified for the instances.
For more information, see About future reservation requests in calendar mode.
Use future reservations with AI Hypercomputer or H4D HPC clusters
Contact your account team and request to reserve GPU instances for large-scale artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) workloads, or for creating a cluster of H4D HPC instances with enhanced cluster management capabilities. After Google creates a draft reservation request for you, submit it for review if everything looks correct. Cloud de Confiance immediately approves the request, and then Compute Engine does the following:
Compute Engine creates on-demand reservations.
Compute Engine reserves your requested resources as close to each other as possible to minimize network latency.
Compute Engine reserves resources with topology-aware scheduling, as well as enhanced monitoring and maintenance.
At the start of your reservation period, you can consume the reservation by creating GPU or H4D instances. At the end of the reservation period, Compute Engine deletes the reservation, and stops or deletes any instances that consume the reservation based on the termination action that you specified for the instances.
For more information, see either of the following:
- For GPU instances: Reserve capacity through your account team in the AI Hypercomputer documentation
- For H4D instances: Reserve capacity through your account team in the Compute Engine documentation
