BigQuery overview
BigQuery is a fully managed, AI-ready data platform that helps you manage and analyze your data with built-in features like machine learning, search, geospatial analysis, and business intelligence. BigQuery's serverless architecture lets you use languages like SQL and Python to answer your organization's biggest questions with zero infrastructure management.
BigQuery provides a uniform way to work with both structured and unstructured data and supports open table formats like Apache Iceberg, Delta, and Apache Hudi. BigQuery streaming supports continuous data ingestion and analysis while BigQuery's scalable, distributed analysis engine lets you query terabytes in seconds and petabytes in minutes.
BigQuery's architecture consists of two parts: a storage layer that ingests, stores, and optimizes data and a compute layer that provides analytics capabilities. These compute and storage layers efficiently operate independently of each other thanks to Google's petabit-scale network that enables the necessary communication between them.
Legacy databases usually have to share resources between read and write operations and analytical operations. This can result in resource conflicts and can slow queries while data is written to or read from storage. Shared resource pools can become further strained when resources are required for database management tasks such as assigning or revoking permissions. BigQuery's separation of compute and storage layers lets each layer dynamically allocate resources without impacting the performance or availability of the other.
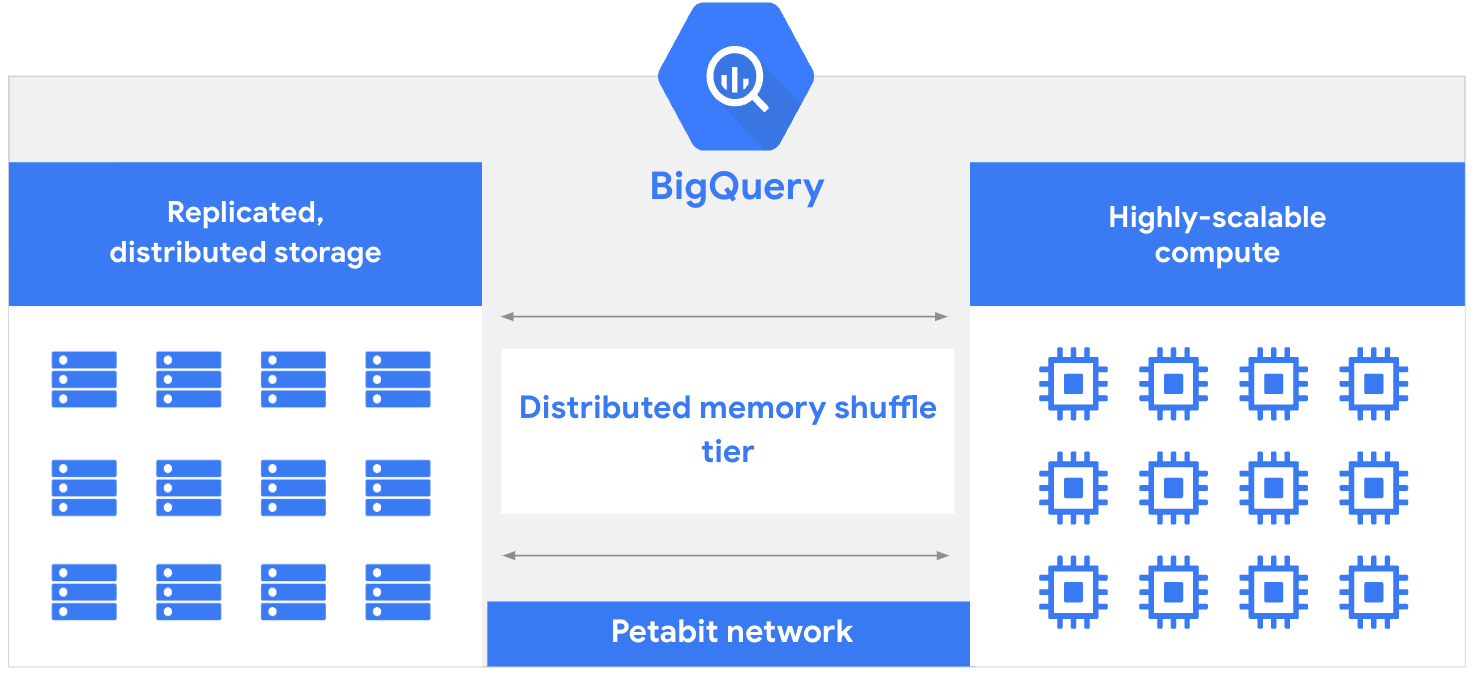
This separation principle lets BigQuery innovate faster because storage and compute improvements can be deployed independently, without downtime or negative impact on system performance. It is also essential to offering a fully managed serverless data warehouse in which the BigQuery engineering team handles updates and maintenance. The result is that you don't need to provision or manually scale resources, leaving you free to focus on delivering value instead of traditional database management tasks.
BigQuery interfaces include Cloud de Confiance console interface and the BigQuery command-line tool. Developers and data scientists can use client libraries with familiar programming including Python, Java, JavaScript, and Go, as well as BigQuery's REST API and RPC API to transform and manage data. ODBC and JDBC drivers provide interaction with existing applications including third-party tools and utilities.
As a data analyst, data engineer, data warehouse administrator, or data scientist, BigQuery helps you load, process, and analyze data to inform critical business decisions.
Get started with BigQuery
You can start exploring BigQuery in minutes.
- Cloud de Confiance console quickstart: Familiarize yourself with the power of the BigQuery Studio.
Explore BigQuery
BigQuery's serverless infrastructure lets you focus on your data instead of resource management. BigQuery combines a cloud-based data warehouse and powerful analytic tools.
BigQuery storage
BigQuery stores data using a columnar storage format that is optimized for analytical queries. BigQuery presents data in tables, rows, and columns and provides full support for database transaction semantics (ACID). BigQuery storage is automatically replicated across multiple locations to provide high availability.
- Learn about common patterns to organize BigQuery resources in the data warehouse and data marts.
- Learn about datasets, BigQuery's top-level container of tables and views.
- Load data into BigQuery using:
- Stream data with the Storage Write API.
- Batch-load data from local files or Cloud Storage using formats that include: Avro, Parquet, ORC, CSV, JSON formats.
For more information, see Overview of BigQuery storage.
BigQuery analytics
Descriptive and prescriptive analysis uses include business intelligence, ad hoc analysis, geospatial analytics, and machine learning. You can query data stored in BigQuery or run queries on data where it lives using external tables or federated queries including Cloud Storage.
- ANSI-standard SQL queries (ISO/IEC 9075 support) including support for joins, nested and repeated fields, analytic and aggregation functions, multi-statement queries, and a variety of spatial functions with geospatial analytics - Geographic Information Systems.
- Create views to share your analysis.
- Business intelligence tool support including 3rd party tools using the Simba ODBC and JDBC drivers for BigQuery
- BigQuery ML provides machine learning and predictive analytics.
- BigQuery Studio makes it easier for you to complete your data analysis and machine learning (ML) workflows in BigQuery.
- Query data outside of BigQuery with external tables.
For more information, see Overview of BigQuery analytics.
BigQuery administration
BigQuery provides centralized management of data and compute resources while Identity and Access Management (IAM) helps you secure those resources with the access model that's used throughout Cloud de Confiance by S3NS.
- Intro to data security and governance helps you understand data governance, and what controls you might need to secure BigQuery resources.
- Jobs are actions that BigQuery runs on your behalf to load, export, query, or copy data.
- Reservations let you switch between on-demand pricing and capacity-based pricing.
For more information, see Introduction to BigQuery administration.
BigQuery resources
Explore BigQuery resources:
- Release notes provide change logs of features, changes, and deprecations.
- Stack Overflow hosts an engaged community of developers and analysts working with BigQuery.
- Google BigQuery: The Definitive Guide: Data Warehousing, Analytics, and Machine Learning at Scale by Valliappa Lakshmanan and Jordan Tigani, explains how BigQuery works and provides an end-to-end walkthrough on how to use the service.
APIs, tools, and references
Reference materials for BigQuery developers and analysts:
- BigQuery API and client libraries present overviews of BigQuery's features and their use.
- DML syntax lets you manage and transform your BigQuery data.
- bq command-line tool reference
documents the syntax, commands, flags, and arguments for the
bqCLI interface. - ODBC / JDBC integration connect BigQuery to your existing tooling and infrastructure.
BigQuery roles and resources
BigQuery addresses the needs of data professionals across the following roles and responsibilities.
Data Analyst
Task guidance to help if you need to do the following:
- Query BigQuery data using interactive or batch queries using SQL query syntax
- Reference SQL functions, operators, and conditional expressions to query data
Use tools to analyze and visualize BigQuery data including Google Sheets.
Use geospatial analytics to analyze and visualize geospatial data with BigQuery's Geographic Information Systems
Optimize query performance using:
- Partitioned tables: Prune large tables based on time or integer ranges.
- Materialized views: Define cached views to optimize queries or provide persistent results.
Data Administrator
Task guidance to help if you need to do the following:
- Manage costs with reservations to balance on-demand and capacity-based pricing.
- Understand data security and governance to help secure data by dataset, table, column, row, or view
- Backup data with table snapshots to preserve the contents of a table at a particular time.
- View BigQuery INFORMATION_SCHEMA to understand the metadata of datasets, jobs, access control, reservations, tables and more.
- Use Jobs to have BigQuery load, export, query, or copy data are actions on your behalf.
- Monitor logs and resources to understand BigQuery and workloads.
For more information, see Introduction to BigQuery administration.
Data Scientist
Task guidance to help if you need to use BigQuery ML's machine learning to do the following:
- Understand the end-to-end user journey for machine learning models
- Manage access control for BigQuery ML
- Create and train a BigQuery ML models
including:
- Linear regression forecasting
- Binary logistic and multiclass logistic regression classifications
- K-means clustering for data segmentation
- Time series forecasting with Arima+ models
Data Developer
Task guidance to help if you need to do the following:
- Load data into BigQuery
with:
- batch-load data for Avro, Parquet, ORC, CSV, JSON formats
- BigQuery Storage Write API
Use code sample library including:
Cloud de Confiance sample browser (scoped for BigQuery)
What's next
- For an overview of BigQuery storage, see Overview of BigQuery storage.
- For an overview of BigQuery queries, see Overview of BigQuery analytics.
- For an overview of BigQuery administration, see Introduction to BigQuery administration.
- For an overview of BigQuery security, see Overview of data security and governance.
